How Greene Tweed Can Help You Get Ready for Hydrogen

This is the second article in a series on Hydrogen Challenges in Aviation sector. Read Part 1
The aerospace industry releases approximately 900 million tons of carbon dioxide1 (CO2) into the atmosphere per year. Though it is currently only 2 to 2.5 percent of the total CO2 emissions released, it is believed the aviation sector could double by 2050. Organizations like International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) have made commitments to reduce aircraft CO2 emissions by 50 percent between 2005 and 2050; and Air Transport Action Group (ATAG) committed to a net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. These commitments have put extreme pressure on aerospace manufacturers to find ways to meet these decarbonization goals quickly.
To reduce climate impact, focus has been placed on using clean technologies like Green Hydrogen (H2) generated by using renewable energy sources, such as Wind and Solar. With studies showing hydrogen can supply up to 3X the energy than what jet fuel offers on a mass basis, it does seem to be a feasible replacement. Unfortunately, hydrogen brings environmental challenges to storing and transporting it, both on the ground and on the aircraft. Research and engineers are exploring advanced materials that can support new aircraft design and operations, airport infrastructure, and fuel supply chain. The biggest challenges that need to be met include:
Permeation
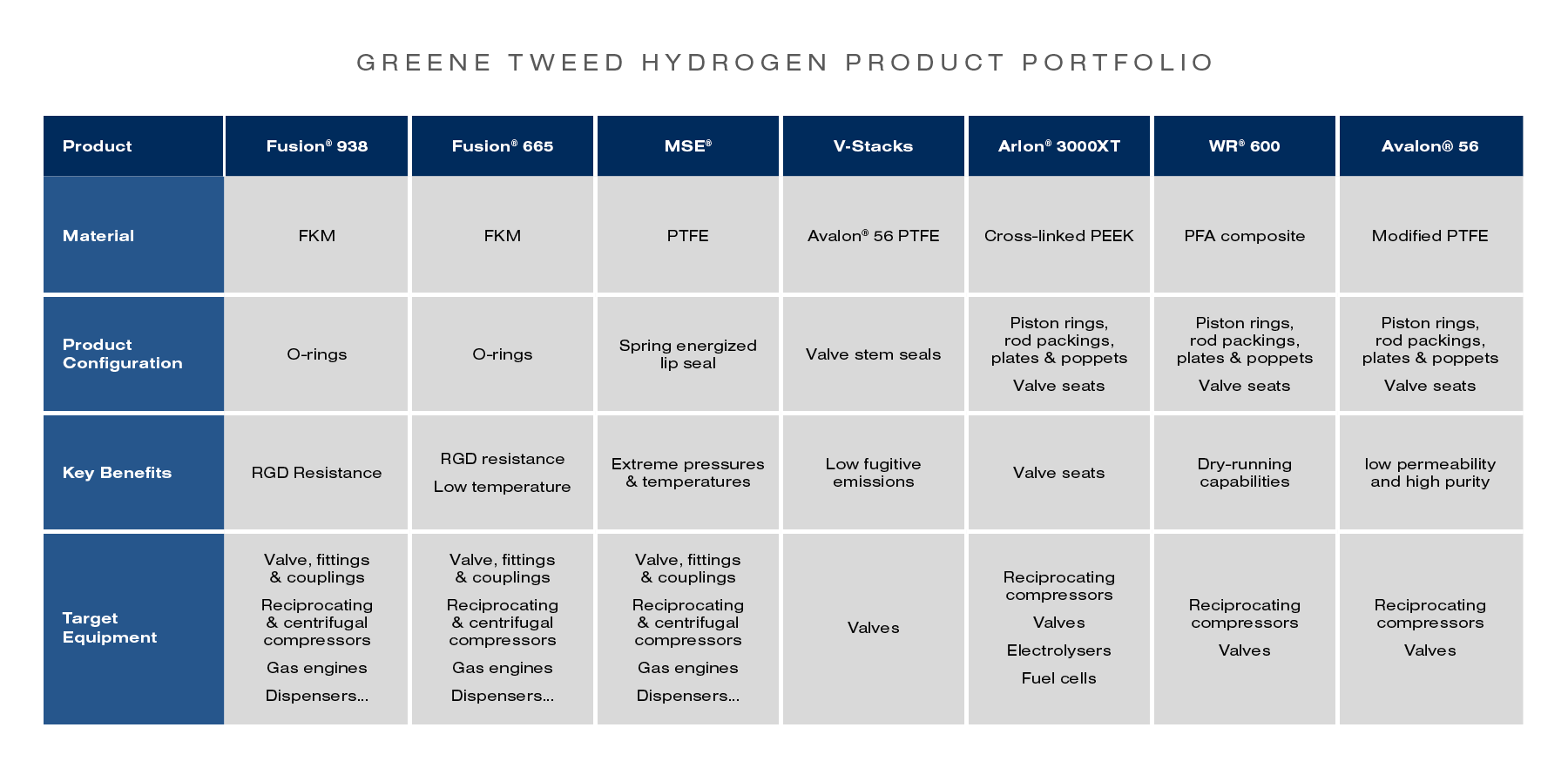
Hydrogen is an exceptionally light, low-density gas. Due to its low molecular form, hydrogen can penetrate any type of polymer materials and metals, creating metal embrittlement issues. When combined with high pressure or pressure cycling applications, hydrogen permeation can generate Rapid Gas Decompression (RGD) issues. Depending on pressure and temperature levels, Greene, Tweed recommends Fusion® 938 O-rings made from high performance FKM or MSE® (Metal Spring Energized) PTFE lip seals. Fusion 938 offers exceptional resistance to hydrogen exposure.
Permeation could also occur at low temperatures. In this case, Fusion® 665 O-rings (FKM) or MSE® lip seals could be a solution of choice. For extreme temperatures found with liquid hydrogen, Greene, Tweed is currently evaluating new sealing solutions and thermal insulation materials.
Lubricity
The low lubricity of hydrogen molecule is a concern in equipment, like valves and compressors, generating excessive wear and friction issues. To overcome these problems, Greene, Tweed offers WR® 600, a PFA composite with unique dry-running properties and Arlon® 3000XT, the only cross-linked PEEK available in the market.

Excessive Weight
Excessive weight has always been a key issue in aerospace applications. Any weight reduction immediately translates into fuel savings. As energy density of hydrogen (by volume) is around three times lower than jet fuel, reservoir sizes must be dramatically increased to transport the same volume of energy with hydrogen as with jet fuel. Therefore, offering lightweight solutions for hydrogen aircraft is even more critical. Greene Tweed’s thermoplastic composite solution, Xycomp® is already extensively used in the aerospace industry as metal replacement.
C/PEEK composites are permeable to hydrogen due to their molecular structure and relatively large space between the molecules and the graphite planes. Such composites cannot accumulate hydrogen as can be seen with metals. Considering that hydrogen embrittlement is therefore not possible with a polymer composite, the use of our Xycomp® solutions makes even more sense in the low-carbon emissions aircraft of the future.
With the global focus on transition to a decarbonized economy, it is becoming imperative for aerospace to find ways to reduce emissions. Greene Tweed is continually developing and testing new materials and technologies to design and manufacture elastomers, thermoplastics, and thermoplastic composite solutions that improve energy efficiency and environmental compliance. Greene Tweed offers in-house design, prototyping, testing, and manufacturing services for custom sealing and bearing solutions. Through customer collaboration, we can develop solutions for each unique application.