How to Choose the Right Seal Material for Your Downhole Application

Buying seals is easy. But finding the seal made of material that’s right for the harsh conditions in your downhole application can be incredibly difficult. There are so many factors to weigh in: Temperature capability, chemical compatibility with the application media, and special considerations like Rapid Gas Decompression (RGD) or steam resistance. Get one of them wrong, and you risk compromising the integrity of your seal. And that’s not all. You need to balance the performance required for your application without unnecessarily increasing the overall cost of ownership.
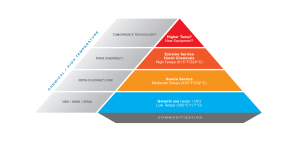
Widely used elastomeric material groups range from those like NBR, HNBR, and EPDM for less extreme applications, up to groups like Fusion® FKM, Xyfluor®, Fluoraz® FEPM, and Chemraz® FFKM for more demanding requirements. Moving up that hierarchy of materials generally provides increasing chemical compatibility and temperature resistance. Compounds within the Fusion™ and Chemraz® families in particular offer specialized compounds which focus on specific challenges such as RGD, steam resistance, or low temperature performance.
Paired with a broad portfolio of materials, Greene Tweed’s seasoned application engineers factor in all provided application parameters when recommending the material and seal geometry most suited to meet the needs of the application. Extra diligence upfront while selecting materials will help to ensure successful operation of equipment in the harshest service environments. Here are a few examples designed to illustrate how the wide Greene Tweed portfolio can be utilized to select the right material for a given application.
Example 1 – Let’s say that the service temperatures in your application will frequently drop as low as 32 °F (0 °C), and the elastomer selected will need to be able to withstand pressures up to 30,000 psi to properly function. And your past testing shows that RGD is a concern. Chemraz® 678 would be the material of choice here, as its low glass transition temperature allows it to perform exceedingly well at high pressures when compared to other low temperature compounds. Further, the ISO23936-2 certification which Chemraz® 678 carries provides assurance of the best performance in conditions where RGD is expected.
Example 2 – If your application requires a compound that is resistant to steam, performs with at least 20 percent concentration of H2S in service, and can operate up to 350 °F (177 °C), you will typically go with Fluoraz® 799. It provides excellent steam resistance and temperature capabilities to match the application, and you might not need to move further up within the Greene Tweed portfolio towards a Chemraz® compound.
Example 3 – In this downhole valve service, temperatures can range up to 450 °F (232 °C), and the seal compound needs to have resistance to hydrocarbons and drilling fluids. Additionally, due to pressure release conditionsring actuation of the valve, RGD resistance is also required. Fusion® 938 provides RGD resistance certified to ISO 23936 and is capable up to the service temperature requirement.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
